Litecoin, one of the most popular cryptocurrencies aside from Bitcoin, is noting a recent severe crash in its hash, almost reaching the 2017 levels.This decline comes just months following the 2019 Litecoin halving event. It raises the question among the community if Litecoin’s network can be jeopardized more easily if the hash rate continues to drop.Litecoin Hash Rate PlungingLitecoin’s hash rate is declining violently over the past six months. The all-time high was reached during the recent July 2019, approximately 523 TH/s. Ever since then, it has been decreasing continuously, and a few days ago, it noted its lowest value for 2019 at 149 TH/s. These numbers represent a total plunge of over 70% in just four months.Litecoin Hash Rate. Source: BitinfochartsThe hash rate is an essential
Topics:
Jordan Lyanchev considers the following as important: AA News, Litecoin News
This could be interesting, too:
Chayanika Deka writes Yuga Labs Secures Major Win as SEC Closes Investigation Without Charges
Andrew Throuvalas writes Bitcoin Soars Back To ,000 After BlackRock CEO Says “Buy The Dip”
Chayanika Deka writes XRP, SOL, and ADA Inclusion in US Crypto Reserve Pushes Traders on Edge
Chayanika Deka writes Why Arthur Hayes Is Bullish on Bitcoin Under Trump’s Economic Strategy
Litecoin, one of the most popular cryptocurrencies aside from Bitcoin, is noting a recent severe crash in its hash, almost reaching the 2017 levels.
This decline comes just months following the 2019 Litecoin halving event. It raises the question among the community if Litecoin’s network can be jeopardized more easily if the hash rate continues to drop.
Litecoin Hash Rate Plunging
Litecoin’s hash rate is declining violently over the past six months. The all-time high was reached during the recent July 2019, approximately 523 TH/s. Ever since then, it has been decreasing continuously, and a few days ago, it noted its lowest value for 2019 at 149 TH/s. These numbers represent a total plunge of over 70% in just four months.
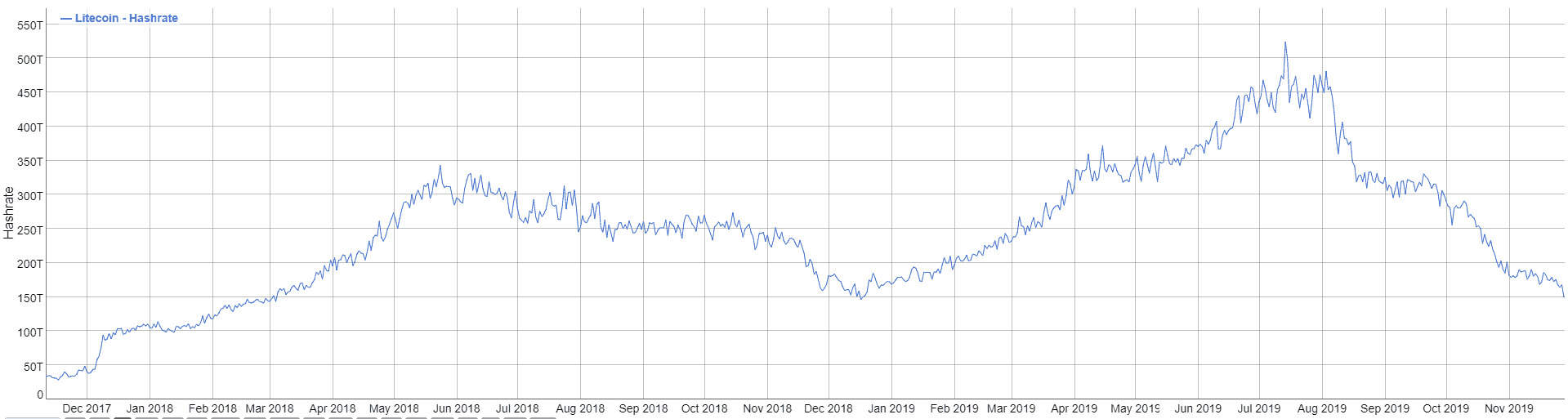
The hash rate is an essential part of the cryptocurrency mechanism. It shows the amount of hash calculated each second over the network. It’s safe to assume that when more miners are mining Litecoin, it would mean more calculations performed per second, resulting in an increasing hash rate. Generally, if it’s declining, it means that fewer people are interested in mining that cryptocurrency, which usually happens if there’s less profitability.
The hash rate is also strongly correlated to the safety and security of the network. When it’s lower, this usually means that it could be more vulnerable to a 51-percent attack.
Simply put, such an attack can occur if a single entity takes control over the hash rate, leading to a disruption in the network. If executed properly, the perpetrator can prevent transactions from being confirmed, exclude miners, reverse transactions, and facilitate double-spending. Back in January 2019, Ethereum Classic reportedly experienced a 51% attack on its network, having 54,200 ETC transferred out of Coinbase.
What Could Be Behind The LTC Hash Decline
Arguably the most plausible reason for the decreasing hash rate could be connected to how miners view and calculate the potential of join forces in the mining efforts. Litecoin noted its block halving in early August, slashing the rewards for miners in half – from 25 LTC per block to 12.5 LTC per block.
At first, miners didn’t seem to be backing off from Litecoin after their rewards were cut in half; however, the declining hash rate may indicate that this is no longer the case.
Interestingly enough, Bitcoin is pre-programmed in a similar way, and its halving is happening in 2020. It may appear as the more attractive cryptocurrency for miners now, so it’s interesting to see how things will play out after the long-anticipated event next year.
